types of vaccine delivery system
After vaccination your muscle cells begin making the S protein pieces and. Other options are a shot under the skin subcutaneous a spray into the nose drops that are swallowed and more.
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer
Most DNA vaccines are delivered by electroporation.

. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and. Improving current delivery methods or designing new ones can enhance the use of existing medications. Live attenuated vaccines fight viruses and bacteria.
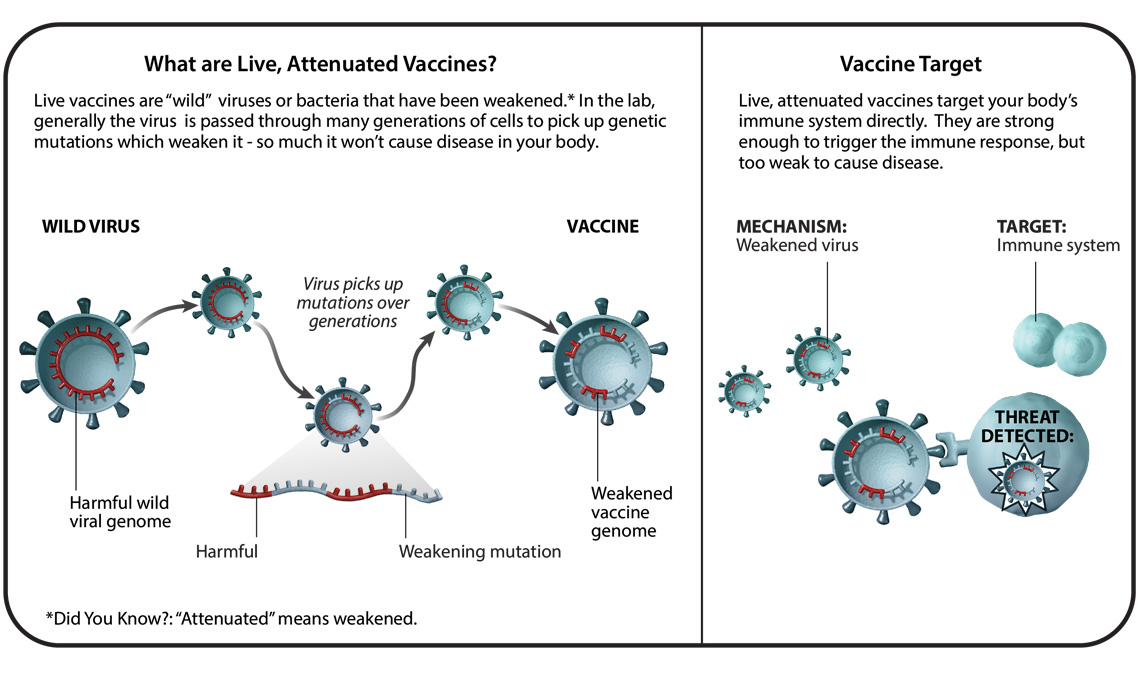
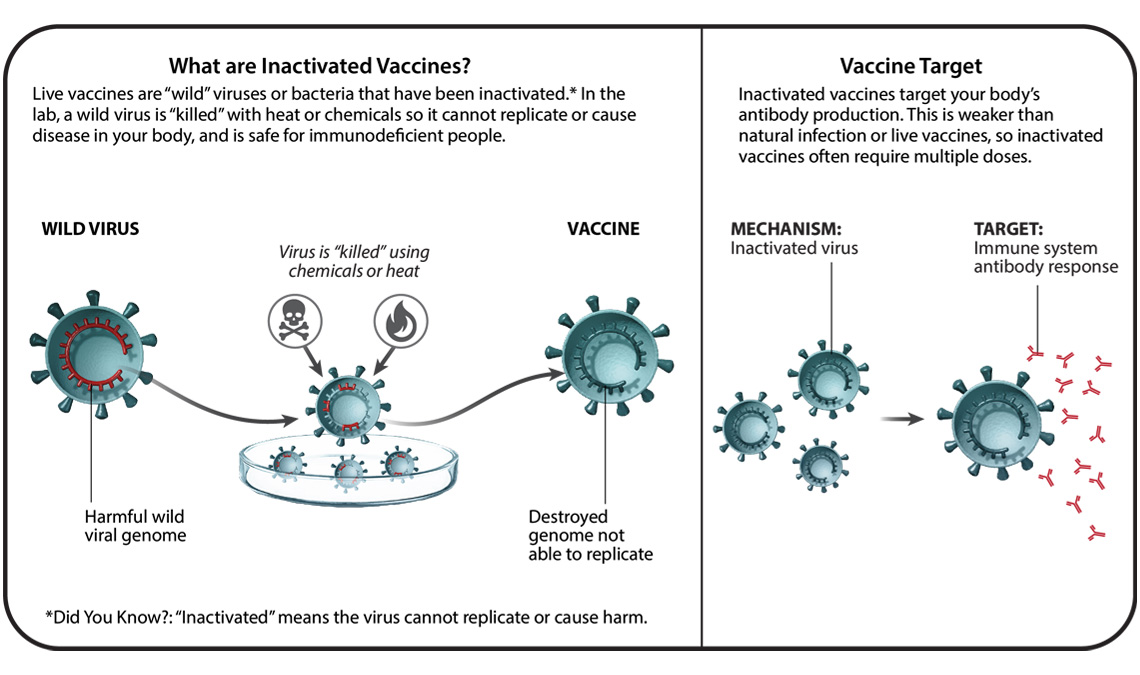
A vaccine delivery system is the means by which the immune-stimulating agent constituting the vaccine is packaged and administered into the human body to ensure that the vaccine reaches the desired tissue. Easy Vax primarily targets the epidermis layer of skin as used in mass-scale prophylactic virus vaccination. Live-attenuated vaccines contain live pathogens from either a bacteria or a virus that have been attenuated or weakened.
Liposomes as a Vaccine Delivery System Semantic Scholar. Delivery systems for mRNA vaccines can be divided into viral- and non-viral vector delivery systems. A prophylactic vaccine that prevents cancers caused by the Human Papillomavirus Types 6 11 16 18 has been approved and in the UK children aged 12-13-years-old are routinely offered this vaccine.
Publication types Review. We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides. The size of the particle systems influences cellular targeting.
Number of doses required. Publication types Editorial MeSH. Abstract Among the various particulate delivery systems liposomesbubble-like nanomicrosized lipidic bilayer structureshave shown great promise as an antigen-carrying vehicle.
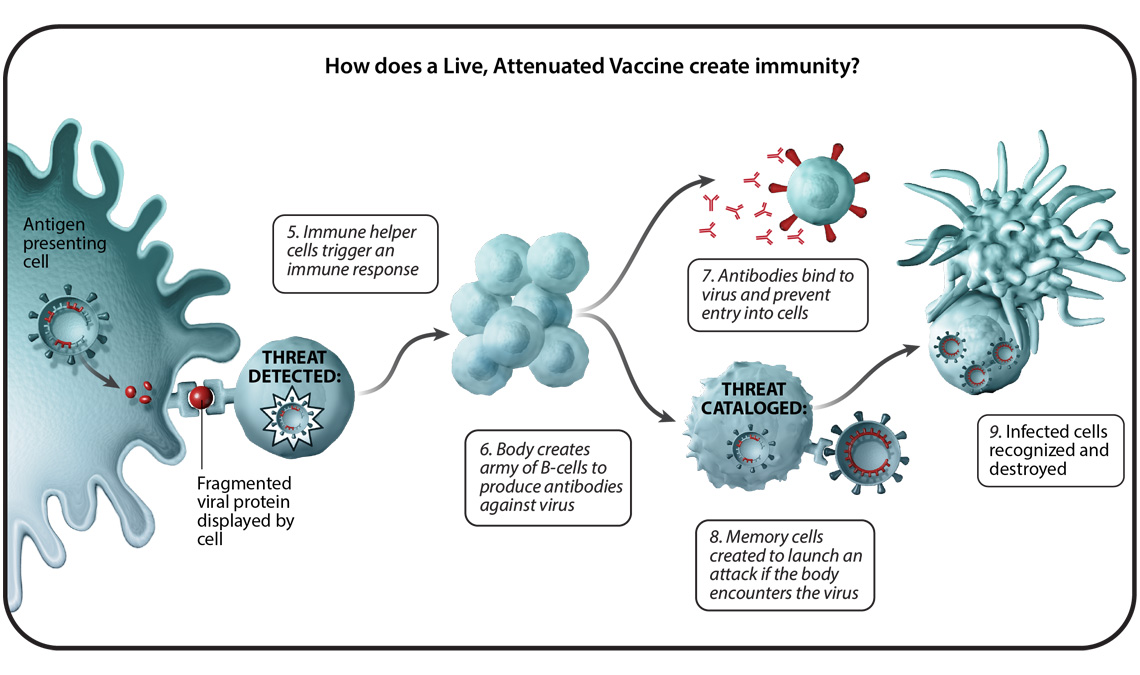
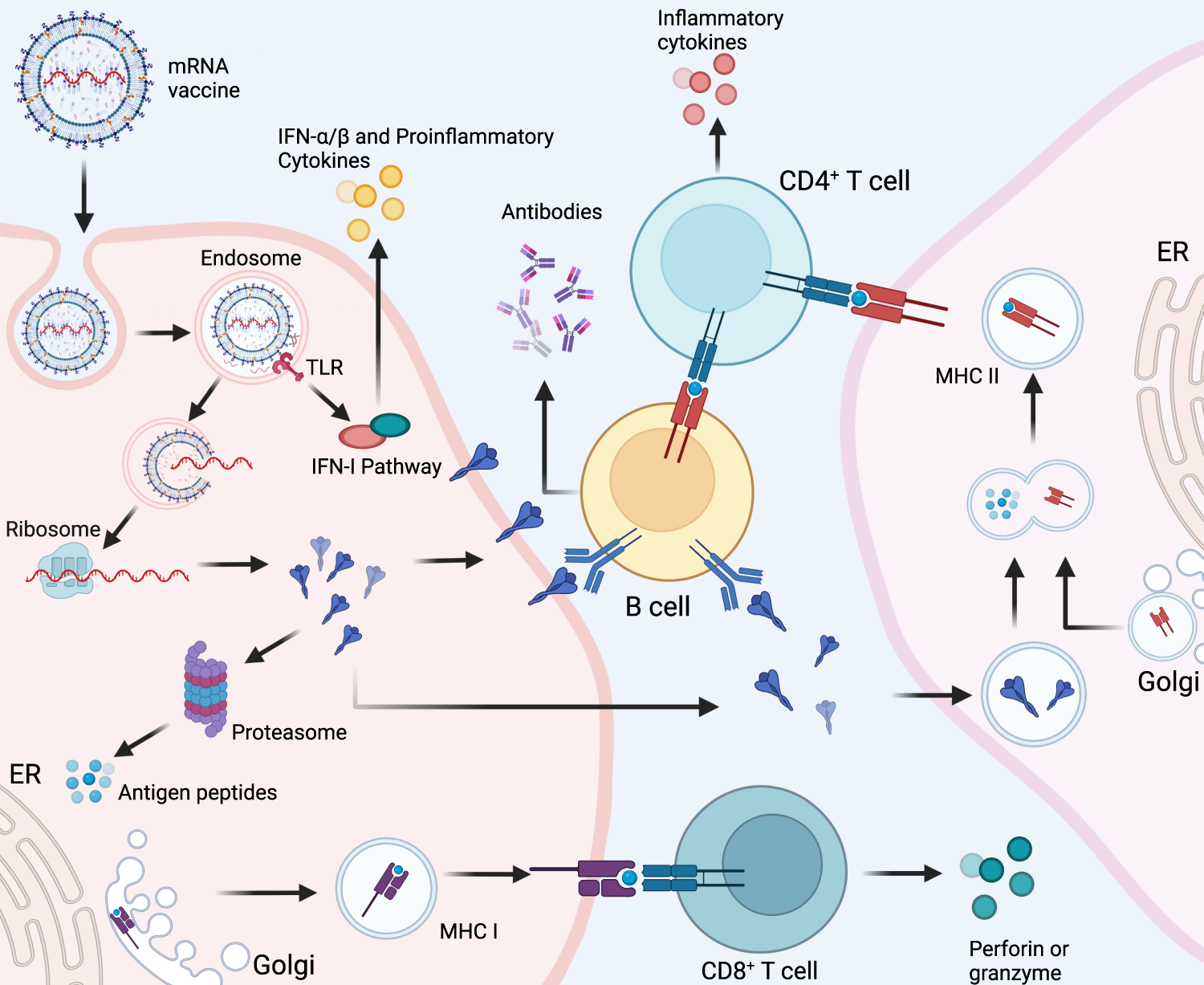
This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus. Vaccines are the preparations given to patients to evoke immune responses leading to the production of antibodies humoral or cell-mediated. Few liposomal vaccines have been introduced to the market.
CDC reports COVID-19 vaccination data online on COVID Data Tracker and in vaccination datasets. Targeting skin cells in particular by Cyto Pulse is more effective than other available intramuscular electroporation systems. These vaccines contain a version of the living virus or bacteria that has been weakened so that it does not cause serious disease in people with healthy immune systems.
The classic example is Jenners use of cowpox to protect against smallpox. Injected into a muscle vaccine molecules stay around for a while and immune cells can easily find them. Today there are five main types of vaccines that infants and young children receive in the US.
Vaccine delivery systems Hum Vaccin Immunother. Vaccinations in the United States. Other licensed vaccines that use this type of technology.
Hepatitis A polio rabies all inactivated type What to know. Delivery of DNA by live vectors is quite efficient relative to naked DNA vaccines. Various gene delivery systems include intracellular bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria monocytogenes Salmonella typhi and Shigella flexneri viruses such as vaccinia adenovirus and avipox and plasmid DNA.
A current example is the use of BCG vaccinemade from Mycobacterium bovisto protect against tuberculosis. MNAs can be easily self-administered without professional training. MNAs are tiny patches of micro-needles about the thickness of a fingernail that can deliver vaccines and other medicines.
With the pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccine delivery systems emerged as a core technology for global public health. MNAs are minimally invasive. The whole virus vaccine uses a weakened or deactivated form of the pathogen that causes COVID-19 to trigger protective immunity to it.
Two clinical vaccine delivery systems have been designed by Cyto Pulse including DermaVax and Easy Vax. This review mainly discusses non-viral vectors which can be further subdivided into lipid or lipid materials and polymer delivery systems. Johnson and Johnson JJ AstraZeneca Sputnik V.
Timely and accurate reporting from jurisdictions drives the information reported by CDC. For some vaccines a different delivery method is better. Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine.
Given that antigen processing takes place inside the cell the intracellular delivery and trafficking of a vaccine antigen will contribute to vaccine efficiency. The main types of COVID-19 vaccines currently available in the US. A COVID-19 Vaccine Delivery Method Guide.
Dime-sized patch of dissolvable microneedles for self-administration of influenza vaccine. This photo shows a r esponder at an. Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or adjuvant-formulated proteins.
Besides simply being compatible with any type of vaccines including the mRNA DNA protein subunit and live attenuated vaccines microneedles are also advantageous because they could replace traditional large needles in parts of the world with a high burden of HIV and other diseases. The subgroup of genetic vaccinesencompass viral vector vaccines RNA vaccines and DNA vaccines. Patches are typically kept on for 1-2 days.
Understanding Six Types of Vaccine Technologies. Recent trends in vaccine delivery systems. The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical.
Author Ryan F Donnelly 1 Affiliation 1 a School of Pharmacy Queens. Microneedle arrays are one example of a new method to deliver medications through the skin. Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also.
Improvement with vaccine delivery systems has led to the generation of nanoparticles self-assembling peptides and needle free delivery. All reported numbers may change over time as updated data are continuously reported to CDC. Or being studied include.
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer
Advances In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Development Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy

All Types Of Covid 19 Vaccines How They Work Animation Youtube
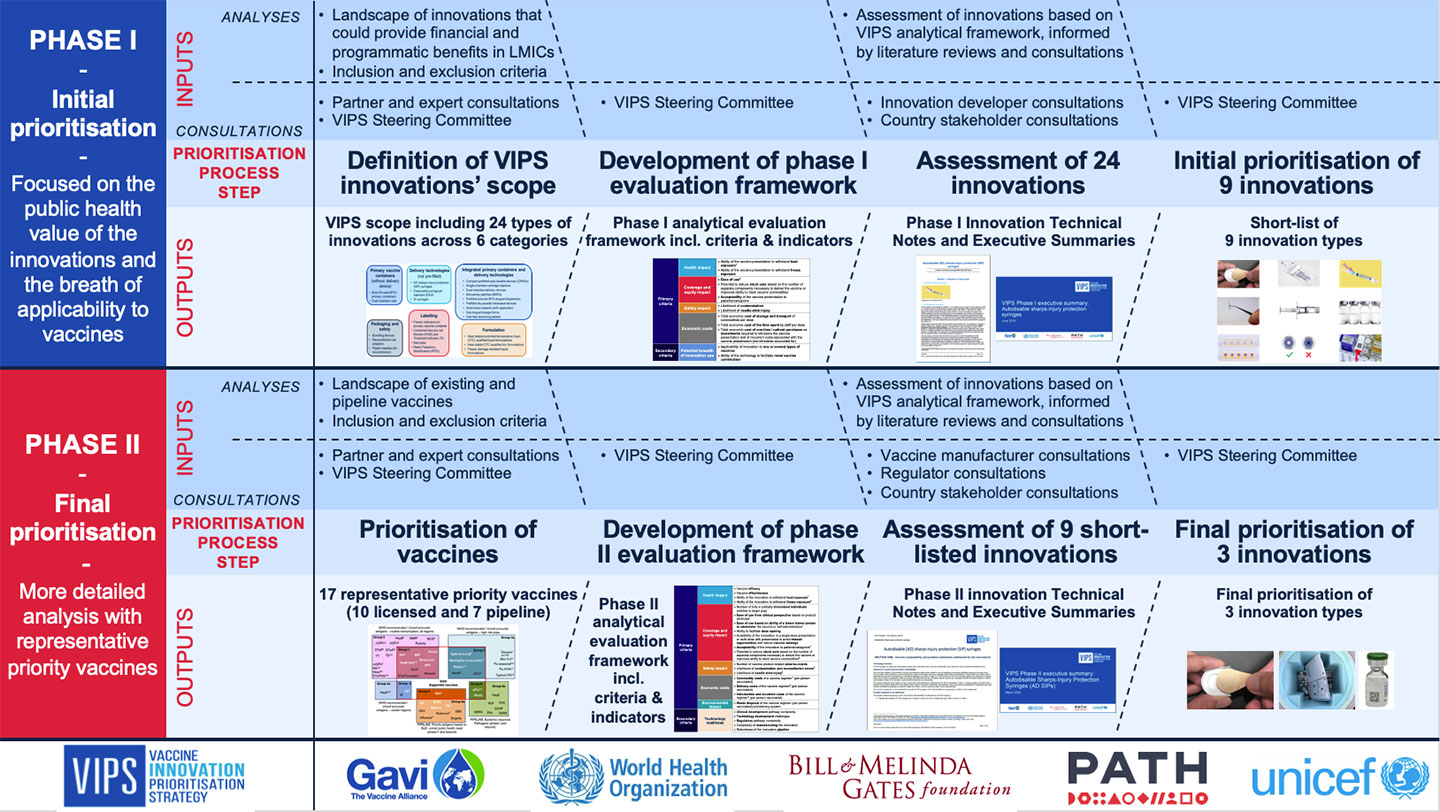
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times
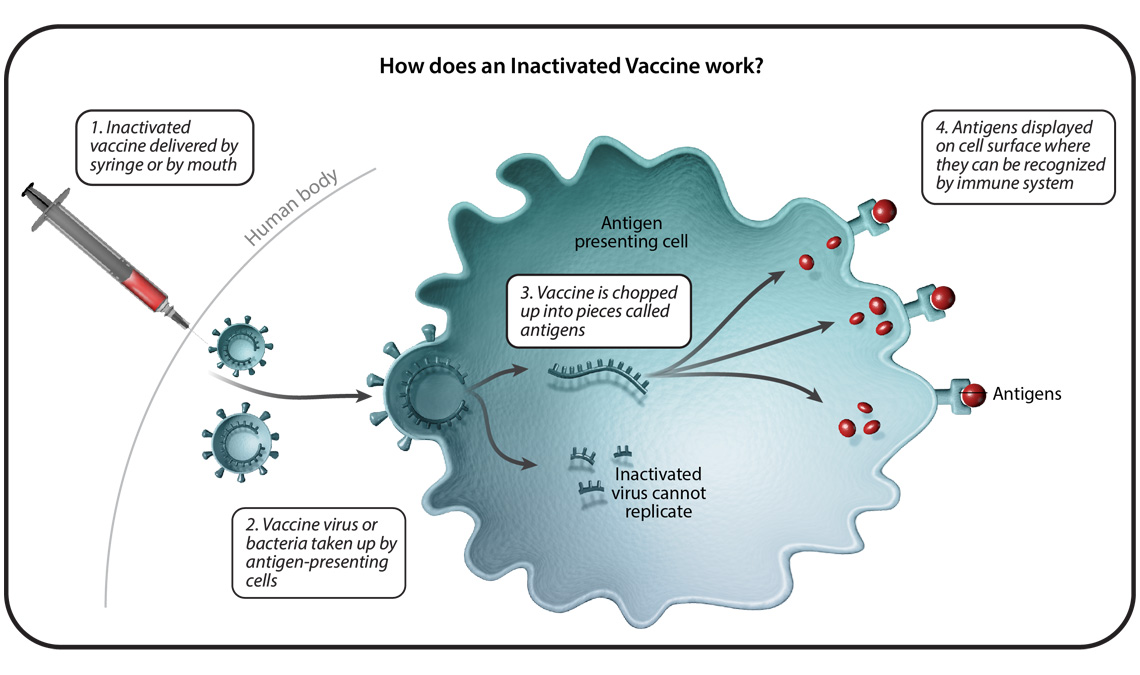
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer
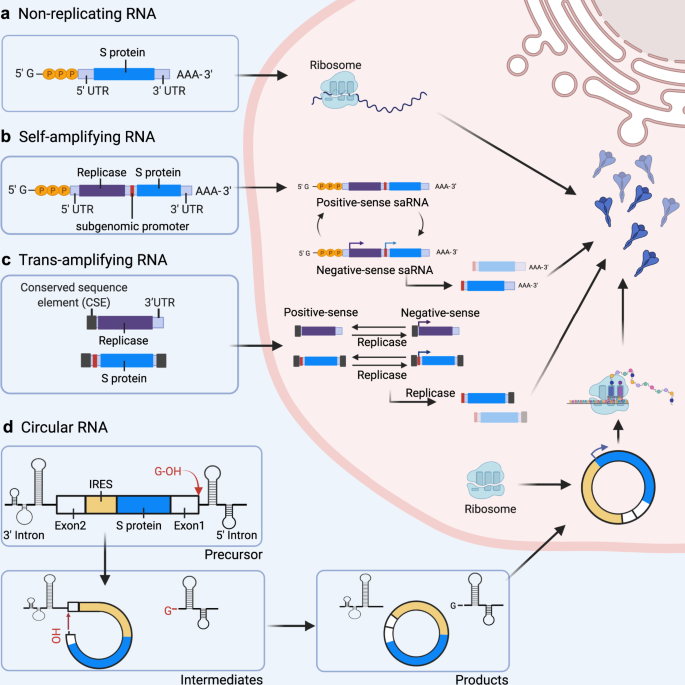
Advances In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Development Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy
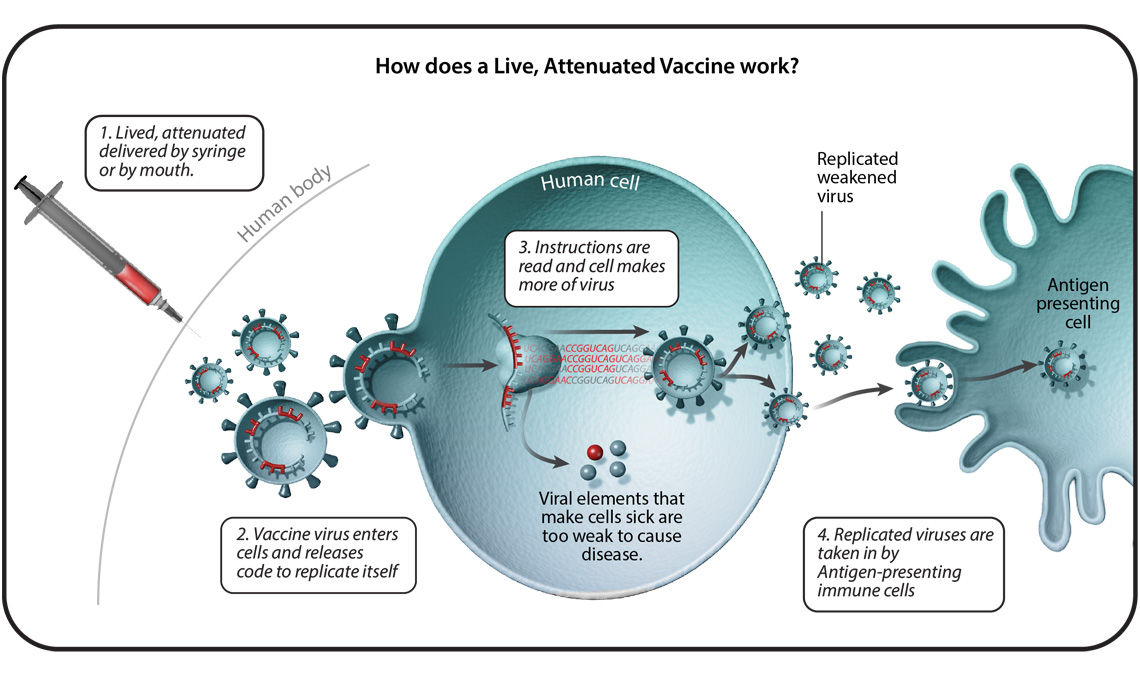
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer

Protein Based Vaccine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Bacterial Vaccine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
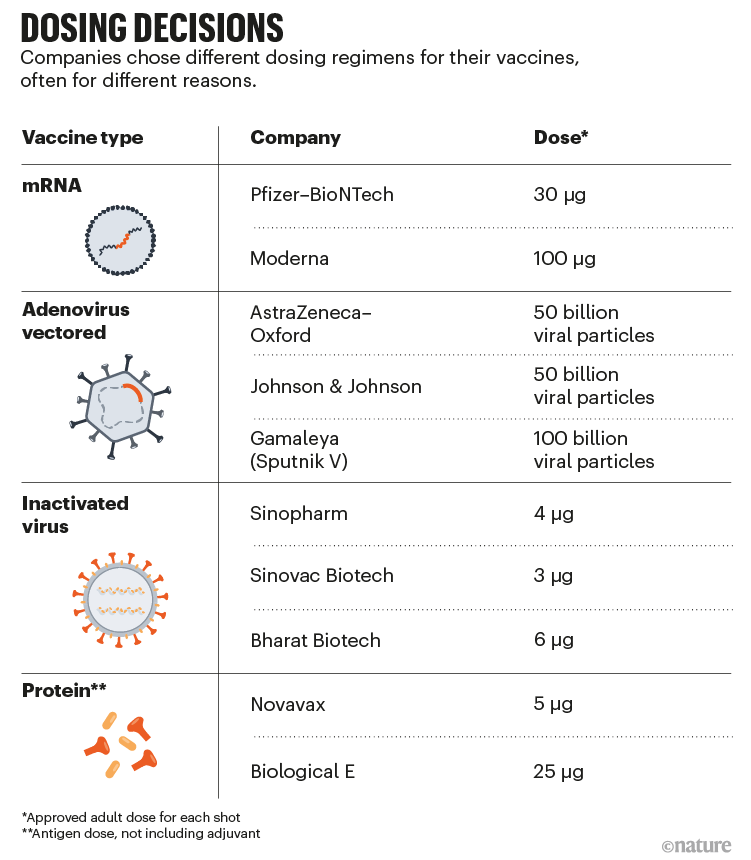
Could Computer Models Be The Key To Better Covid Vaccines
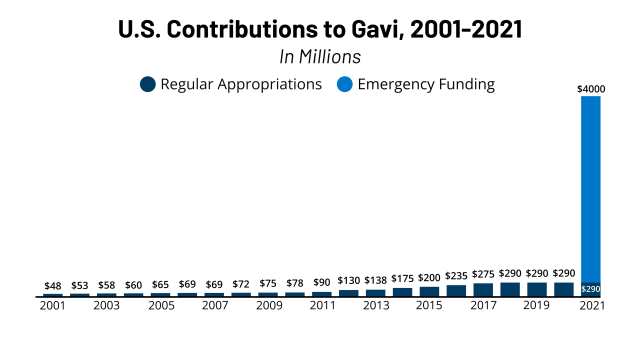
The U S Government Gavi The Vaccine Alliance Kff
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines Plos Global Public Health

Inactivated Virus Vaccine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
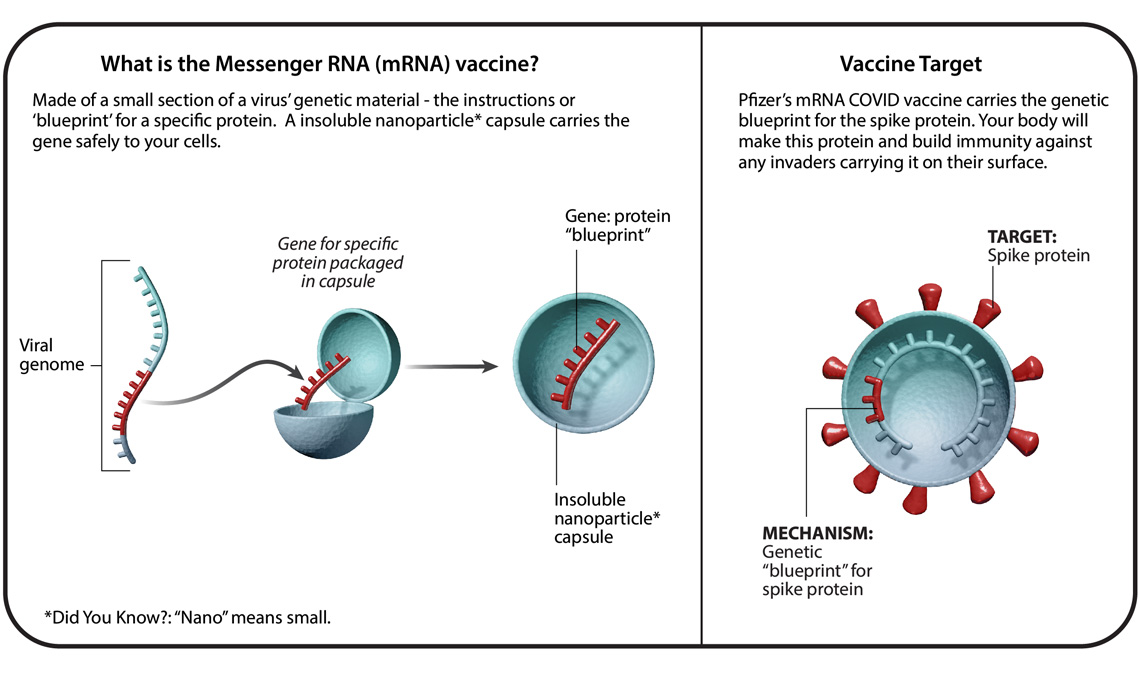
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer
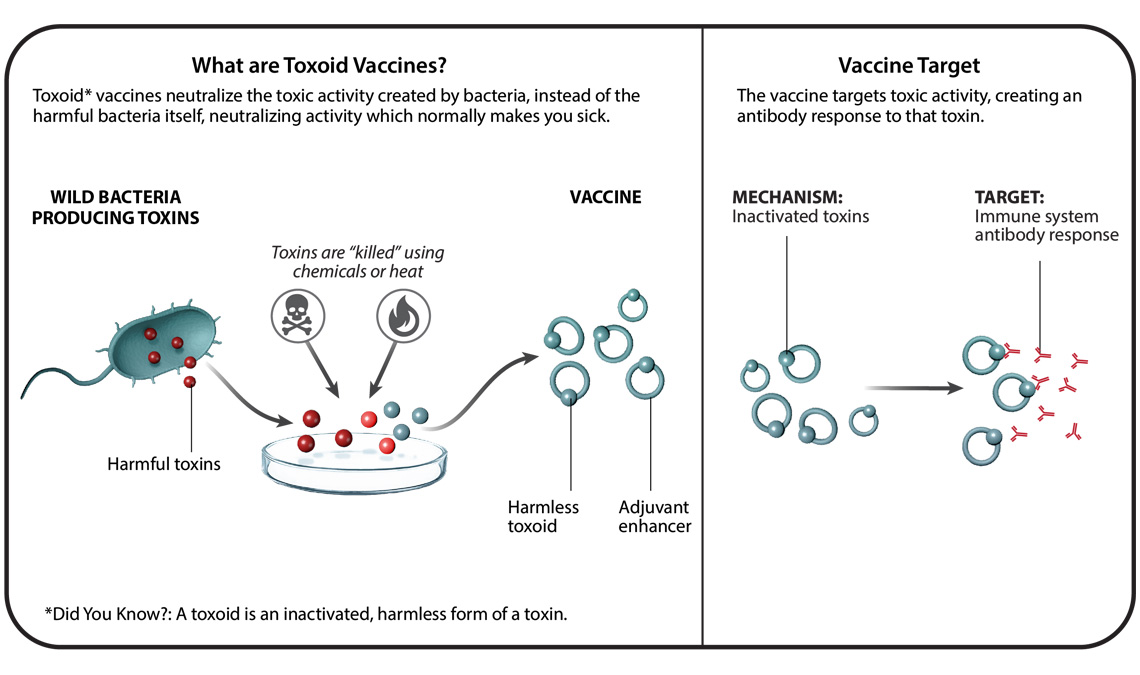
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer
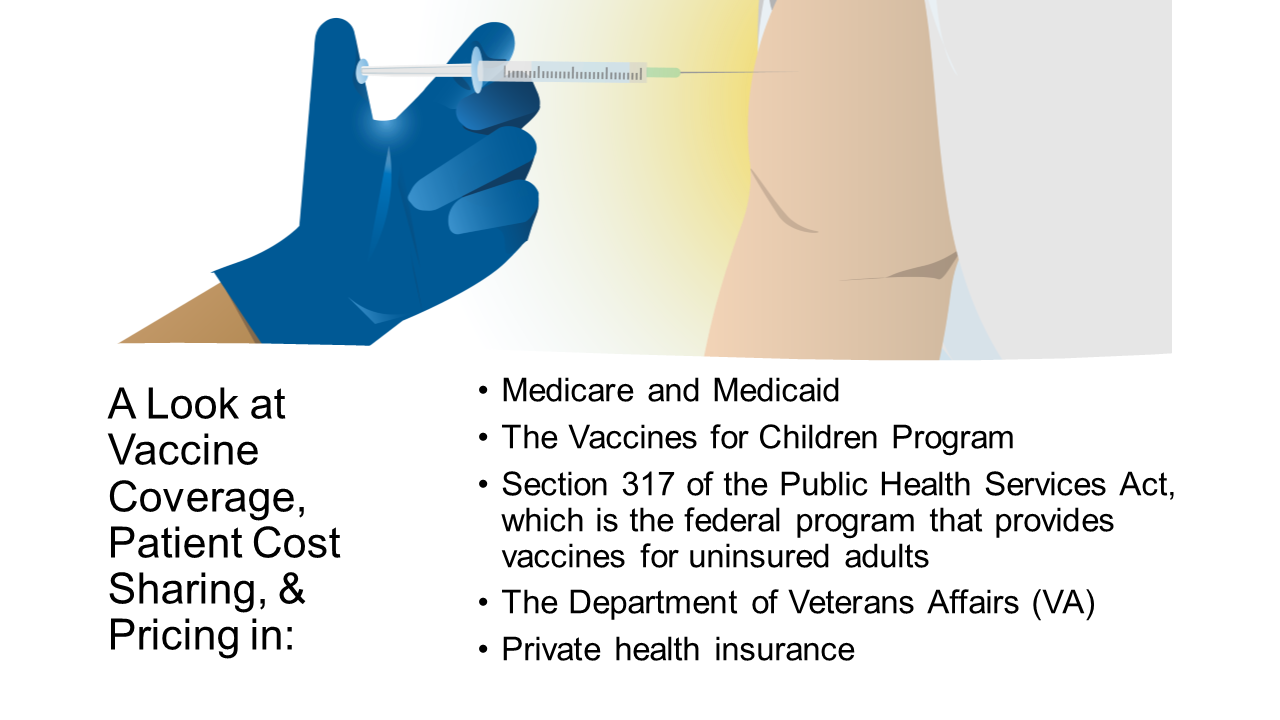
Vaccine Coverage Pricing And Reimbursement In The U S Kff
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer

How The Pfizer Biontech Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times